-
SR.navbar.languageswitch.texthide
-
SR.navbar.languageswitch.texthide
-
SR.navbar.languageswitch.texthide
-
SR.navbar.languageswitch.texthide
-
SR.navbar.languageswitch.texthide
-
SR.navbar.languageswitch.texthide
-
SR.navbar.languageswitch.texthide
-
SR.navbar.languageswitch.texthide
-
SR.navbar.languageswitch.texthide
-
SR.navbar.languageswitch.texthide
-
SR.navbar.languageswitch.texthide
-
SR.navbar.languageswitch.texthide
- Puxadores industriais
-
Automação
-
União de tubo
-
Tecnologia de superfícies
-
 Revestimento em pó
Revestimento em pó -
 Galvanização
Galvanização -
 Anodização
Anodização -
 Anodização especial
Anodização especial -
 Polimento electrolitico de produtos em aço indoxidável
Polimento electrolitico de produtos em aço indoxidável -
 Decapagem pura de componentes em aluminio
Decapagem pura de componentes em aluminio -
 Aluminium Conversion Coatings
Aluminium Conversion Coatings -
 Quantitades pequenas - Elaboração individual
Quantitades pequenas - Elaboração individual -
 Esmerilar, escovar e polir
Esmerilar, escovar e polir -
 Decapagem com esferas de vidro e granalha
Decapagem com esferas de vidro e granalha -
 Rotopolimento (trovalização)
Rotopolimento (trovalização)
-
- Tratamento mecânico
-
Novidades
-
Empresa
- Início >>
- Tecnologia de superfícies >>
- Galvanização
Galvanização
Brief Specialist Information
For the designer in mechanical engineering and precision mechanics, but also for the interested professional buyer, knowledge of the physical relations involved in galvanization is of great use.
Buscar
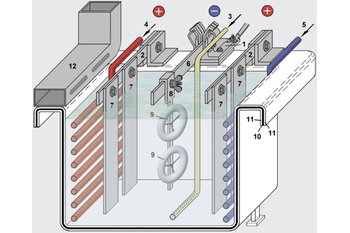
Electrogalvanizing of rack objects
For all kinds of machine components and technical items electrogalvanizing with varied chromating is still the most frequently-employed protection against corrosion.
Buscar
Zinc / iron alloy plating
Galvanic zinc alloy plating has for years been established as a high-quality corrosion-control measure for iron and steel products.
Buscar
Electrogalvanizing of loose bulk goods
Articles of this kind (e.g. screws, nuts, bolts, smaller stampings etc.) are usually processed in rotating barrel electroplating machines (s. fig.).
Buscar
Pearl-brightness chromium plating
The term is misleading because to be technically correct this process involves nickel plating with pearl-brightness (satin finish) and subsequent chromium plating.
Buscar
High-gloss chromium plating
To be technically correct, this process – as is the case with pearl-brightness chromium plating – involves high-gloss nickel plating and subsequent chromium plating.
Buscar
High-gloss and semi-gloss nickel plating
For many technical items one of the two above types of nickel plating is preferential to chromium plating for one or more of the following reasons:
Buscar
Galvanic tin-plating
Tin is a silvery white, lustrous metal, whose shine does not become dulled, even during storage. It is highly resistant to atmospheric influences. With the exception of nitric acid, there are hardly any dilute inorganic and organic acids that attack it.
Buscar
Contacto
Rohde AG
Industriestrasse 9
D - 37176 Nörten-Hardenberg
Tel.: +49 (0) 5503 9860-0
Fax: +49 (0) 5503 9860-11
Opening hours (CET)
| Mon. - Thur. | 07.15 - 15.45 |
| Fri. | 07.15 - 15.30 |